Traditional drug discovery often relies on single endpoint assays using visual markers, which can be challenging to quantify and limited in their ability to capture the complexity of biological systems. RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq) offers a more holistic approach by providing a rich dataset on gene expression changes in response to perturbations.
RNA-Seq allows researchers to determine RNA molecules in a sample at the moment of sampling. The transcriptome is a highly dynamic cellular feature that opens up a world of discovery potential. RNA-Seq provides a comprehensive and unbiased view of gene expression in all its complexity enabling researchers to:
- Quantify gene and transcript expression levels
- Identify alternative splicing events and transcript isoforms
- Detect gene fusions associated with diseases
- Study small regulatory RNAs and their targets
- Analyze gene expression from single-cell transcriptomes
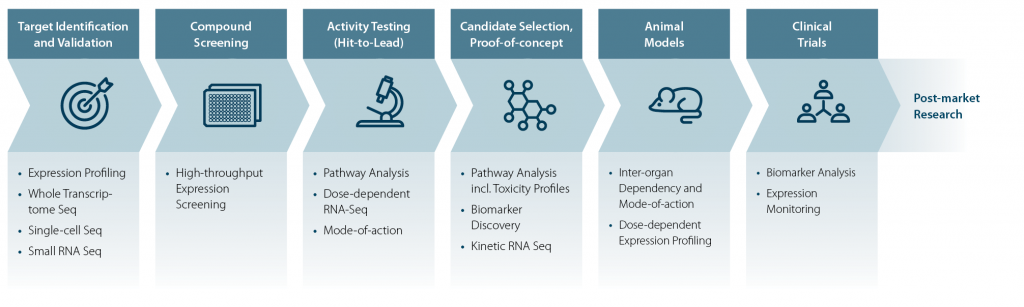
The Drug Discovery and Development Process
The pharmaceutical industry and biopharma companies are continuously advancing approaches to accelerate drug discovery and development – a complex and elaborate process spanning various phases (Fig. 1; Hughes et al., 2011; Singh et al., 2023).
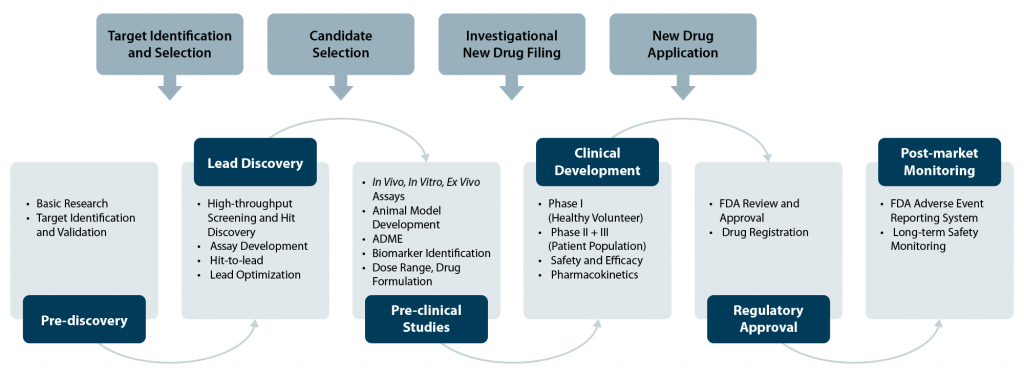
Pre-discovery
During this initial stage, fundamental research is conducted with the aim to understand specific disease mechanisms. Scientists use “omics” technologies to identify and validate new potential drug targets based on their role in the disease mechanism.
Lead Discovery
In this phase, researchers prepare and screen compound libraries to identify molecules with the potential to interact with the target and produce a therapeutic effect. This stage involves extensive experimentation, high-throughput screening, assay development, and lead optimization.
Preclinical Studies
Promising candidates undergo a series of rigorous testing in vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo in animal models to clarify the mode of action, assess toxicity, validating efficacy, and pharmacological properties. Drug dosage and formulation are also determined during this phase.
Clinical Development
During clinical development, the drug candidate is studied in humans to evaluate drug safety, efficacy, and determine side effects. It consists of several stages (Phase I, II, and III) with increasing numbers of participants – ranging from healthy volunteers to patients and assessing different population groups (e.g., by gender, age, ethnicity, etc.).
Regulatory Approval and Post-market Surveillance
Once clinical trials demonstrate the drug’s safety and efficacy, a new drug application is filed for regulatory approval. Following approval and market launch, the drug is continuously monitored for adverse effects and long-term safety.
Applications for RNA-Seq in Drug Discovery and Development
In recent years, high-throughput RNA sequencing (HTS RNA-Seq) has emerged as a powerful tool used in the early stages of the process – specifically during early drug discovery and assay development. By providing a comprehensive view of gene expression, RNA-Seq enables researchers to identify novel drug targets, assess compound efficacy, and uncover unexpected drug mechanisms. RNA sequencing is also extremely useful to study the candidates during the preclinical studies elucidating the mode of action, primary and secondary effects or for example inter-organ mechanisms in animal models and for ADME (Adsorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion) testing. Further, RNA-Seq is also applied during clinical trials to study candidate effects in healthy volunteers and patient population studies in Phases II and III. Our blog about the importance of RNA-Seq in drug discovery and development delivers a comprehensive overview of the use and advantages of RNA sequencing in the different stages.
Target identification and validation build on basic research following fully elucidated networks and modes of action for the drug target of interest. Pharma and biotech companies can default to basic research institutes or academic research to assess novel “druggable” targets for validation.
RNA-Seq for Hit Screening and Lead Discovery / Optimization
During the early or lead discovery phase, researchers commonly prepare and screen compound libraries to identify molecules with the potential to interact with the previously defined target. The compounds are first evaluated based on the ability to produce a therapeutic effect which classifies them as an active compound – the so-called ‘hit’ molecule (Hughes et al., 2011). This stage involves large-scale screening approaches in cell-based assays. Throughout the process, the compounds are tested using various assays to ensure researchers are focusing on compounds which produce a consistent, reproducible and robust effect on the target. Several factors are key to consider for successful assay development. RNA-Seq methods which produce robust and highly consistent results independent of the experimenter and over time, as well as adequate controls are paramount.
Key Factors for Successful Assay Development
A robust assay is essential for efficient drug discovery. Several critical factors must be considered during development.
- Pharmacological Relevance: The assay should accurately reflect the disease state and be capable of identifying compounds that target the desired biological pathway.
- Reproducibility: Consistent results across different assay plates, testing days, and the entire drug discovery program are paramount for reliable data generation.
- Assay Quality: The assay’s performance should meet predefined standards, including the accurate behavior of control compounds.
- Robustness: The assay should be insensitive to variations in assay conditions, such as solvent concentrations, to ensure reliable data interpretation.
Many RNA-Seq technologies require a multitude of steps to complete the workflow which can increase the variability of the assay. RNA-Seq methods with fewer steps and short, streamlined workflows are particularly suited for drug discovery assay development. In addition, as very high sample numbers are required to be processed in early phases, the methods need to be extremely scalable and cost-effective. For this reason, sample-barcoded 3’ mRNA-Seq technologies that allow early pooling and processing of samples in batches (pools) are the method of choice. They deliver unbiased, accurate gene expression information, and allow to perform pathway analyses to confirm the desired effect on the biological target and its network. In addition, 3’ mRNA-Seq approaches are hypothesis-free, previously unknown effects or influences on other molecules can also be discovered. In contrast, targeted RNA-Seq technologies which are also commonly used rely on the pre-definition of the molecules of interest which should be investigated. This approach is particularly cost-efficient but misses effects on molecules which are not included in the selection and cannot discover new interactions or unknown effects.
High-throughput Screening
Ultra-high throughput drug discovery screens can utilize hundreds of thousands to millions of samples in order to analyze entire compound libraries for single compounds and combinations and identify molecules with the desired activity. Due to the massive sample numbers and nature of these screens, classical phenotypic assays are still heavily utilized to keep the costs per sample in a reasonable range. Thus, any RNA-Seq based method that could potentially be used has to be highly cost-efficient to be used during this step. While the benefits of including a transcriptomic read-out in the early stages are vast, the costs are often prohibitive. Miniaturizing screens to work with lower cell numbers, minute amounts of compound per condition and using highly sensitive 3′ mRNA-Seq library preparation directly from the cell lysate can provide a solution. Not only can the costly RNA extraction be skipped, 3′ mRNA-Seq preps with high sensitivity can also be analyzed at low read depth (e.g., 100 K – 500 K reads) for pathway-level information. LUTHOR HD Pool for example enables sample processing directly from lysates for low cell numbers at a cost of down to ~2 USD per sample. Due to sample-barcoding and early pooling, the method is extremely scalable (>36,000 samples per sequencing run) and ultra-sensitive. The compatibility with low cell numbers allows to miniaturize cell-based assays and compound treatments and enables screens directly on primary cells, neurons, or stem cells.
For more information, download our brochure: High-throughput RNA-Seq Directly from Lysates.
Selective Assays
Following the ultra high-throughput assay, selected subsets of molecules with potential target activity are further characterized, in vitro assays are employed to assess transport and toxicology, and / or tissue-based approaches are supplemented to gather further insights into the response towards the desired in vivo effect. Selective screens of subsets, mechanistic secondary assays and additional tests using protein-assays, structural approaches and more sophisticated model systems serve to further characterize the leading compounds (drug leads) and select a candidate for further pre-clinical studies. At this stage, RNA-Seq can also be supplemented to add a further layer of information and to complement phenotypic assays. As the sample number is reduced at this stage, the cost for these experiments is no longer prohibitive and RNA-Seq can be implemented more easily.
During all of the stages in the early drug discovery process, Contract Research Organizations (CROs) and companies specialized in sequencing services provide expertise and know-how to support pharma and biotech by conducting NGS experiments, aiding assay development or conducting cell-based and protein assays to facilitate drug development.
Outsourcing NGS Sequencing Assays: Benefits of Partnering with a Trusted Service Provider
While many research institutions and company labs have embraced RNA sequencing for target identification and validation, as well as high-throughput compound screening and selective screens for lead discovery and selection, not all possess the necessary infrastructure or expertise to fully leverage its capabilities. This is where specialized service providers can offer solutions tailored to the need for the specific screens. By partnering with experienced sequencing service providers, laboratories can gain access to state-of-the-art equipment, specialized personnel, and can obtain results much faster. In addition, data analysis and interpretation is of growing importance to increase efficiency and tap into the complex information NGS sequencing has to offer. Various Service providers offer end-to-end solutions integrating data visualization for faster turn-around, or enable data interpretation through specialized data analysis providers for their clients. This collaborative approach allows researchers to focus on their core competencies while outsourcing the complex and time-consuming aspects of NGS RNA sequencing and if needed, data analysis. Another reason to outsource these specialized assays is that it allows pharma and biotech companies to save costs associated with the maintenance of in-house RNA-Seq labs, equipment, consumables and specialized personnel – all in all, reducing overhead costs for the discovery project. In addition, Service providers often operate at much larger scale for NGS projects and can offer lower costs per sample.
At Lexogen NGS Services, several projects have been successfully realized throughout the drug development process contributing to the advancements of numerous promising therapies. Some exemplary case studies are shown below (Fig. 3).
Benefits of Outsourcing RNA-Seq to a Trusted Partner
Partnering with a specialized RNA-Seq service provider offers several advantages for drug discovery projects:
- Expertise and experience: Service providers have extensive knowledge and experience in RNA-Seq technologies, ensuring optimal experimental design and data analysis. Many trusted service providers additionally offer upfront consultation.
- State-of-the-art equipment: Access to the latest sequencing platforms and equipment for high-quality data generation without any upfront capital investment.
- Time and cost savings: Outsourcing RNA-Seq can save time and resources by eliminating the need for in-house infrastructure, hiring and training employees and establishing novel technologies and workflows.
- Data analysis support: Service providers can offer comprehensive data analysis services, including bioinformatics tools and expertise. Alternatively, dedicated data analysis service providers with specialized tools for drug discovery and development provide data interpretation at highest standards and allow integration of multi-omics data sets to connect genome, transcriptome, and proteome. For example, BigOmics Analytics is dedicated provider for data analysis, empowering clients with a specific “Omics Playground” for drug discovery including Pathway and Biomarker analysis, as well as Drug Connectivity visualization tools.
- Quality assurance: Partnering with a reputable service provider ensures adherence to quality standards and robust, reliable results.
- Flexibility: Service providers can tailor their offerings to meet specific project needs and timelines.
Overall, outsourcing RNA-Seq can be an extremely beneficial strategic decision for drug discovery projects, providing access to expertise, cost-efficiency, flexibility, and quality assurance. By leveraging the expert services of specialized providers, researchers can accelerate their drug discovery efforts and improve their chances of success.
Summary
RNA-Seq has become a powerful and versatile tool to advance drug discovery and development. The applications of RNA sequencing are diverse and beneficial for all stages of the discovery process, ranging from understanding disease mechanisms to developing personalized therapies. Transcriptome analysis is commonly used to identify target genes for therapeutic intervention with novel compounds, or to investigate drug resistance and how to overcome it with combinatorial or personalized approaches.
Many pharmaceutical companies and research institutions partner with specialized service providers to fully leverage the expertise and resources needed for RNA sequencing. In addition, many service providers enable researchers to complete projects in shorter time by offering convenient end-to-end solutions, consultation, data analysis support, and workflow or pipeline transfers. In summary, outsourcing can help reduce costs, accelerate timelines, and ensure high-quality results.
References
Hughes, J.P., Rees, S., and Kalindjian, S.B.; Philpott, K. L.2011162 (2011). Principles of early drug discovery. British journal of pharmacology 162, 1239-1249. DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.01127.x.
Singh, N., Vayer, P., and Tanwar, S.; Poyet, Jean-Luc; Tsaioun, Katya; Villoutreix, Bruno O. (2023). Drug discovery and development: introduction to the general public and patient groups. Front. Drug Discov. 3. DOI: 10.3389/fddsv.2023.1201419.
Written by Dr. Yvonne Goepel